[Paper]
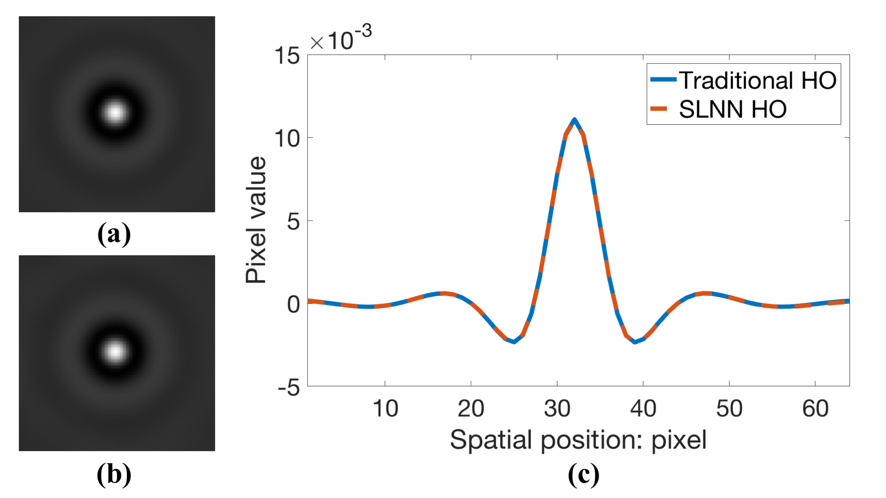
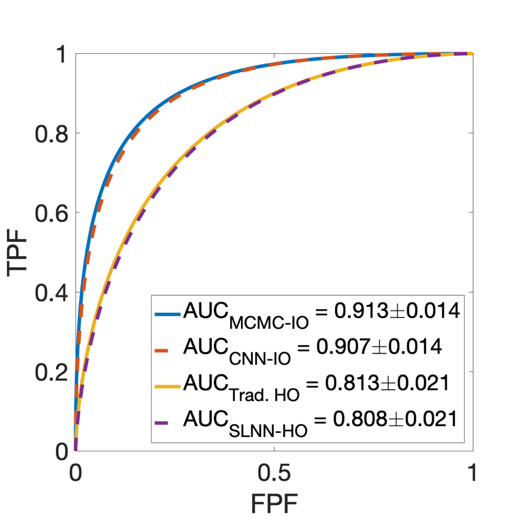
It is widely accepted that optimization of medical imaging system performance should be guided by task-based measures of image quality (IQ). Task-based measures of IQ quantify the ability of an observer to perform a specific task such as detection or estimation of a signal (e.g., a tumor). For binary signal detection tasks, the Bayesian Ideal Observer (IO) sets an upper limit of observer performance and has been advocated for use in optimizing medical imaging systems and data-acquisition designs. Except in special cases, determination of the IO test statistic is analytically intractable. Markov-chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) techniques can be employed to approximate IO detection performance, but their reported applications have been limited to relatively simple object models. In cases where the IO test statistic is difficult to compute, the Hotelling Observer (HO) can be employed. To compute the HO test statistic, potentially large covariance matrices must be accurately estimated and subsequently inverted, which can present computational challenges. This work investigates supervised learning-based methodologies for approximating the IO and HO test statistics. Convolutional neural networks (CNNs) and single-layer neural networks (SLNNs) are employed to approximate the IO and HO test statistics, respectively. Numerical simulations were conducted for both signal-known-exactly (SKE) and signal-known-statistically (SKS) signal detection tasks. The considered background models include the lumpy object model and the clustered lumpy object model. The measurement noise models considered are Gaussian, Laplacian, and mixed Poisson-Gaussian. The performances of the supervised learning methods are assessed via receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analysis and the results are compared to those produced by use of traditional numerical methods or analytical calculations when feasible. The potential advantages of the proposed supervised learning approaches for approximating the IO and HO test statistics are discussed.
Publications
- Zhou, W., & Anastasio, M. A. (2018, March). Learning the ideal observer for SKE detection tasks by use of convolutional neural networks (Cum Laude Poster Award). In Medical Imaging 2018: Image Perception, Observer Performance, and Technology Assessment (Vol. 10577, p. 1057719). International Society for Optics and Photonics.
- Zhou, W., Li, H., & Anastasio, M. A. (2019). Approximating the Ideal Observer and Hotelling Observer for binary signal detection tasks by use of supervised learning methods. IEEE transactions on medical imaging, 38(10), 2456-2468.
- Zhou, W., Li, H., & Anastasio, M. A. (2019, March). Learning the hotelling observer for ske detection tasks by use of supervised learning methods. In Medical Imaging 2019: Image Perception, Observer Performance, and Technology Assessment (Vol. 10952, p. 1095208). International Society for Optics and Photonics.